CARDIOPULMONARY RESUSCITATION
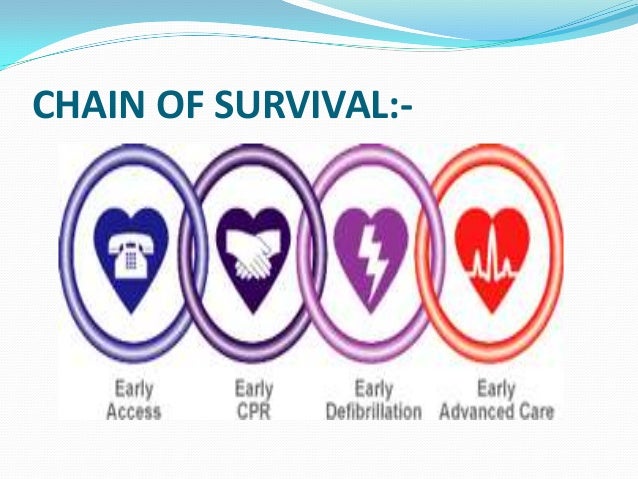
What is CPR?
CPR is a combination of rescue breathing (mouth-to-mouth resuscitation) and chest
compressions to restore circulation of oxygen-rich blood to the brain. Without oxygen,
permanent brain damage or death can occur in less than 8 minutes
Definition :
Cardiopulmonary
resuscitation (CPR) is a combination of mouth-to-mouth resuscitation and chest
compressions that delivers oxygen and artificial blood circulation to a person
who is in cardiac arrest. It can be life-saving first aid.
Indications of CPR:
Cardiac
Arrest
- Heart disease – the most common cause of cardiac arrest
- Ventricular fibrillation (VF)
- Ventricular tachycardia (VT)
- Asystole
- Pulse less electrical activity
Respiratory
Arresst
THIS CAN BE DUE TO FOLLOWING:
- Drowning
- Stroke
- Foreign body in throat
- Smoke inhalation
- Drug overdose
- Electrocution or injury by lightening
- Suffocation
- Accident, injury
- Coma
- Epiglottis paralysis.
- Hypoglcemia
- Electrolyte Imbalane
Fluid Balanace:
- Hypovolemic Shock
- Hemorrhage
Neurologic Indications :
- Massive CVA
Poisons or Substance Overdose:
- CO Poisoning
- Proipanolol Overdos
Purpose of CPR:
- To maintain an open and clear airway (A).
- To maintain breathing by external ventilation (B).
- To maintain Blood circulation by external cardiac massages (C).
- To save life of the Patient.
- To provide basic life support till medical and advanced life support arrives
Warning Sings of Cardio Pulmonary Arrest:
- Loss of consciousness
- Convulsions
- Apnea or stridor
- Dilated pupils
- Absence of heart rate or weak thready pulse
- Cyanosis
- Hypothermia
Procedure of CPR:
Check for response by tapping on shoulder & saying "HEY ARE YOU OK?''
Airway :
- Head Tilt Jaw Left Manoeuvre :While pushing the forehead back tilt the chin forward
- Jaw Thrust Manoeuvre : This is to be performed while neck injury by pushing the face forward with index finger by holding cheeks with both the hands
Breathing : Look, Listen & Feel for breathing & pulse. Breathing can be initiated by :
- Mouth to Mouth Ventilation
- Mouth to Mask Ventilation
- Bag Mask Ventilation
Circulation : Check for pulse:
- Adult : Carotid artery
- Infant : Brachial artery
Chest Compressions :
Interlock fingers of both the hand by placing heel of domninant hand on the centre of chest & other hand on its top.
For infants : Place 2 fingers or 2 thumbs on the breast bone & give downward thrust by tilting the head back of infant
Universal Compression to Ventilation Ratio:
- For Adult - 30:2
- For Infant & Children - 15:2
- For Newborn - 3:1
Recommended Depth of Compression:
- In adult & children- 5 cm [2 inches]
- In infants - 4 cm [1.5 inches]
Rate of Compression = 100/min
Complications of CPR:
- Rib & Spleen fracture
- Pneumothorax & Hemothorax
- Injury to diaphragm, Myocardial muscle
- Aspiration
- Vomiting
Medical & Nursing Management during CPR
- Adrenaline: to enhance cerebral and myocardial blood flow by preventing arterial collapse
- Noradrenaline : to restore normal circulation
- Atropine: to block vagal tone completely & enhances automacticity and conduction of both sinoatrial and atriventricular node.
- Amiodarone or Lidocaine : to dilate coronary artery leading to vasodilatation and reduction in afterload and systemic blood pressure.
- Calcium Gluconate :enhances the contractile force of cardiac muscle
- Sodium Bicarboinate :to alkalinaze urine in drug over dose
- Magnesium : to stabilize myocardial cell membrane
- Intubation & Oxygenation
- Administer IV fluids
- Documentation of Vitals & urine output
- Maintain appropriate ventilation



No comments:
Post a Comment